Phone:
(701)814-6992
Physical address:
6296 Donnelly Plaza
Ratkeville, Bahamas.
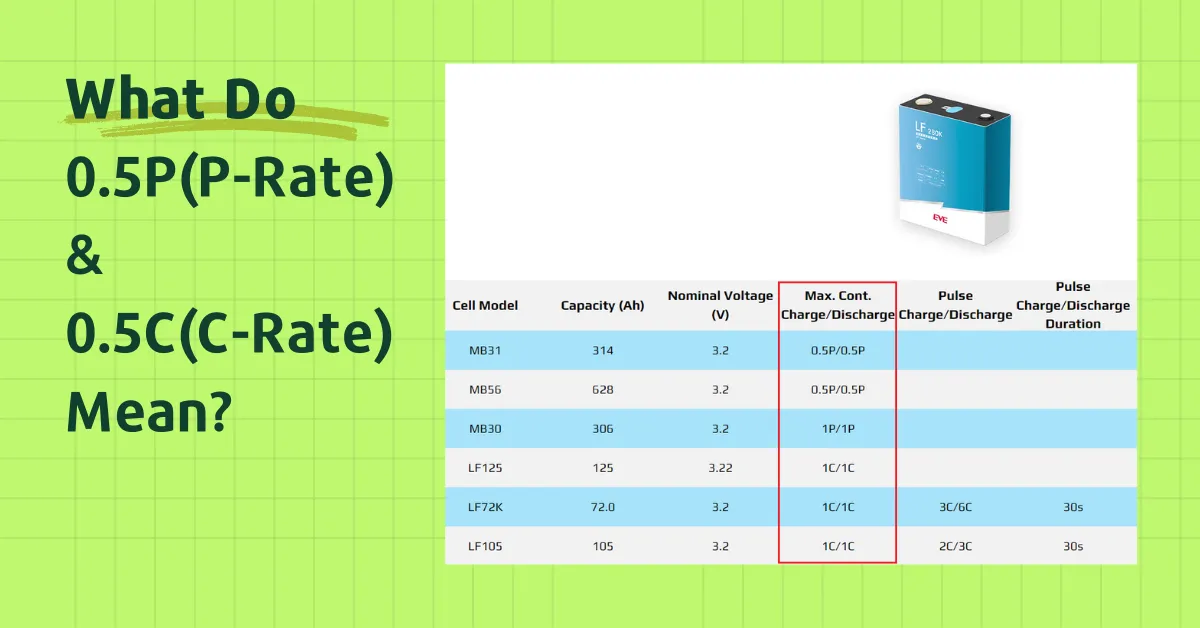
We frequently come across terms like 1C, 0.5C, 0.5P, and 0.25P when perusing battery datasheets, specifications, and manuals. These designations are not just jargon but are key to understanding a battery’s performance and safe operating limits. Grasping the distinction between P-Rate and C-Rate is essential for anyone looking to harness the full potential of their batteries without causing damage. Let’s demystify these terms and see how they apply to battery specifications with some real-world examples.
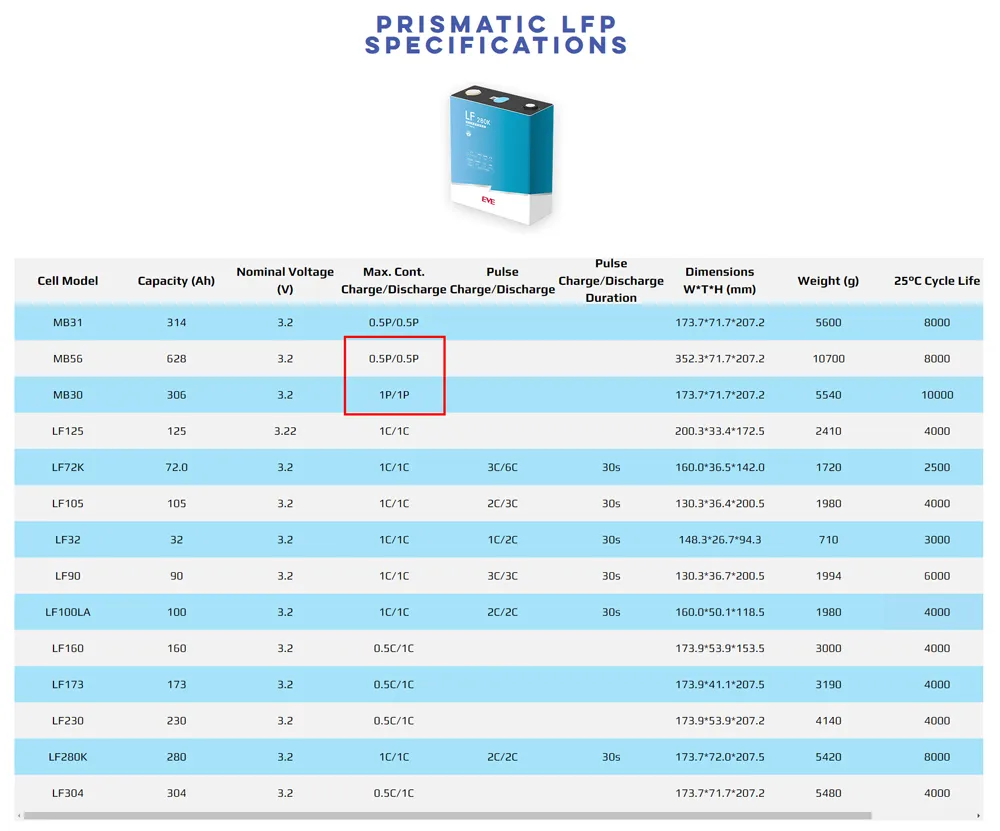
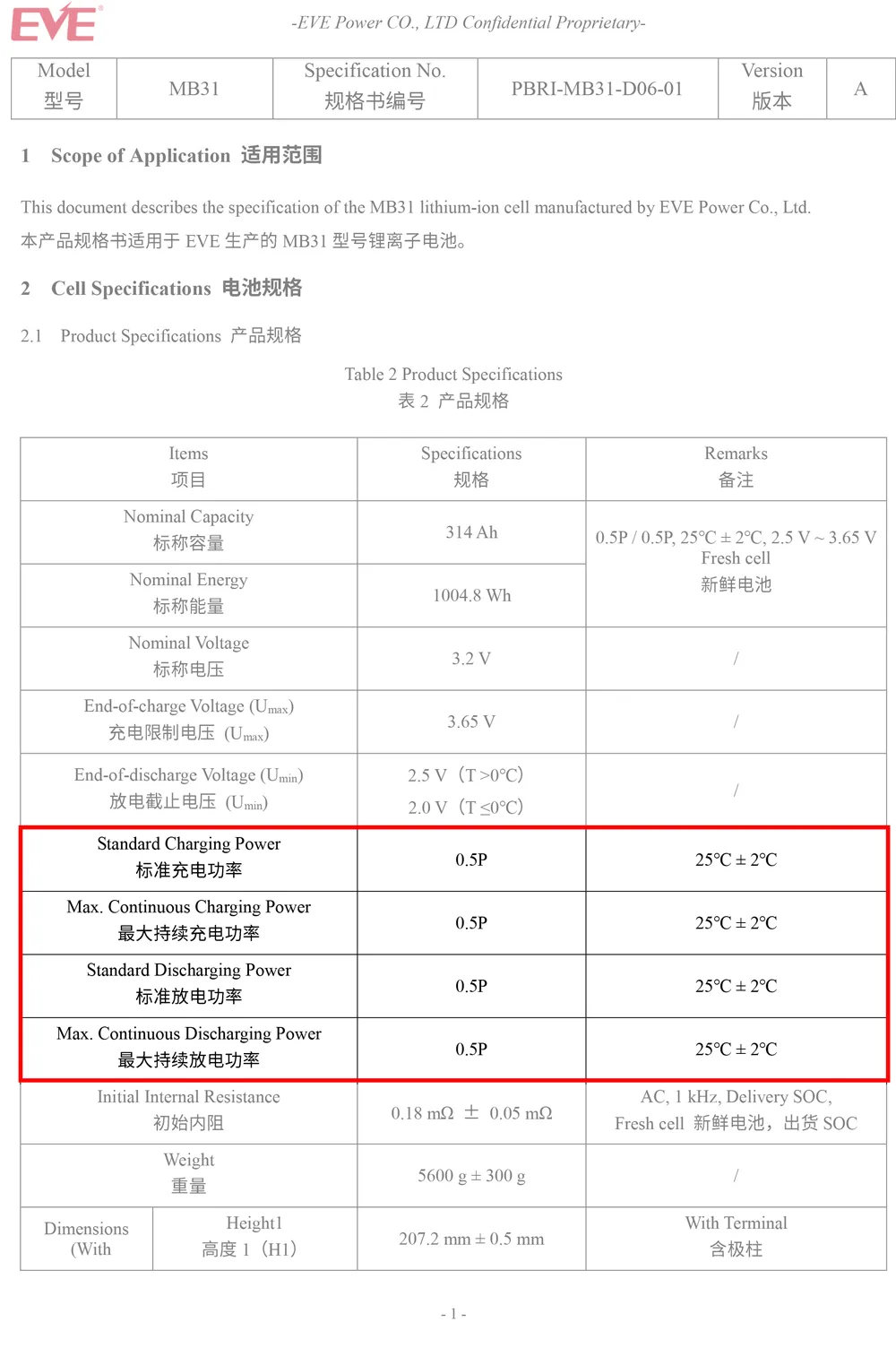
The ‘P’ in P-Rate stands for power, and it’s a measure of the battery’s power output relative to its total energy capacity. The term ‘0.5P’ means the battery is delivering power at half of its maximum capacity. For instance, if a battery’s energy capacity is 1004.8 Wh and it’s being charged or discharged at 502.4 W, it’s operating at a 0.5P rate. This is a critical specification for applications requiring high power output, ensuring the battery can meet the demand without being overdriven.
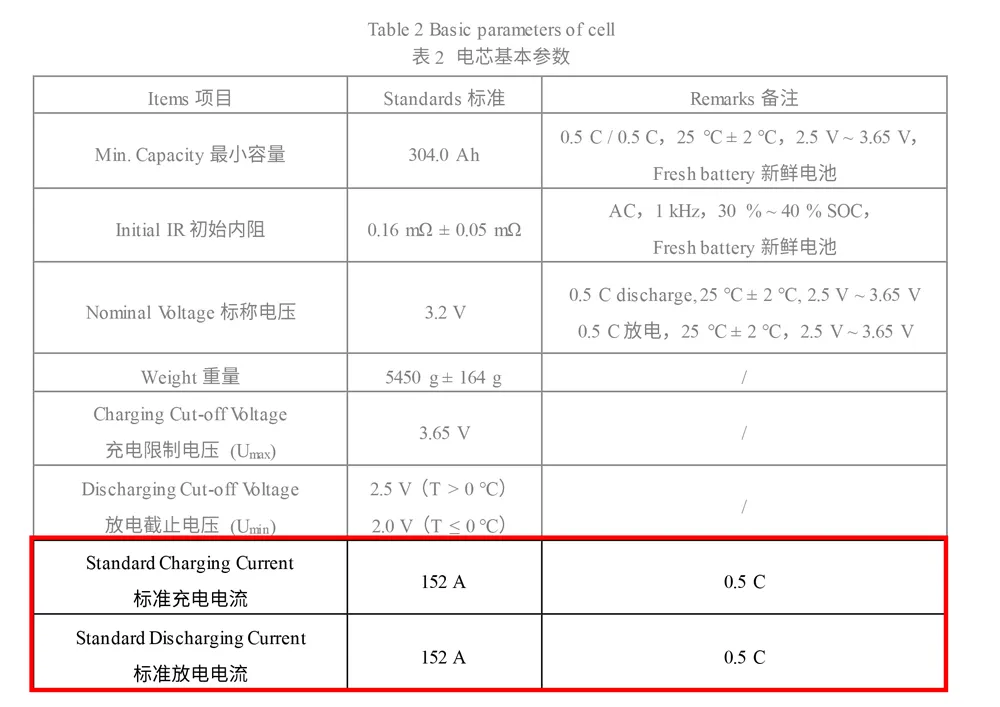
The ‘C’ in C-Rate stands for the battery’s charging rate, which is the ratio of the charging current to the battery’s capacity. A 0.5C rate indicates that the current used to charge the battery is half of its total capacity. For example, if a battery has a capacity of 304 Ah, a 0.5C charging rate would be 152 A. If the capacity decreases to 280 Ah, the charging current at 0.5C would be 140 A. This is vital for determining how quickly a battery can be charged without causing damage or inefficiency.
While both P-Rate and C-Rate are ratios of half capacity, they refer to different aspects of battery performance:
Understanding 0.5P (P-Rate) and 0.5C (C-Rate) in battery specifications is essential for selecting the right battery for your needs and using it safely and efficiently. P-Rate focuses on power delivery, while C-Rate is about charging speed. By using real examples from battery specifications, we can clearly see how these rates inform us about the battery’s capabilities and limitations.